Ver.2.0
User Manual
Configuration & Settings
NOTE: These settings should only be altered by a qualified radio service technician.
CONTENTS:
1. Transmit (TX) Control
There are two basic types of transmitter control available in ComTekk DISPATCHER: a) Tone remote control or b)Serial control. Tone control is compatible with any EIA standard tone termination panel, and is normally used in situations where the radio equipment is installed some distance from the dispatch operator position. Connection is made with either a single-line (2-wire) or 2-line (4-wire) twisted pair cable. DISPATCHER requires a 4-wire connection for both transmit (TX) and receive (RX) functionality.
NOTE: Tone Remote control may not function properly in Windows Vista.
Serial Push-to-Talk (PTT) control is accomplished by utilizing the DTR or RTS pins on a RS-232 port to toggle a relay or transistor circuit. A serial to USB adaptor may be used for newer computers with no serial port. ComTekk offers a computer-radio interface unit which provides a convenient method of connection. Distance between computer and transmitter is generally limited to about 25 feet or 8 meters. Length may be extended by use of larger gage wiring, or other means.
For wiring details, see the Installation section of this manual.
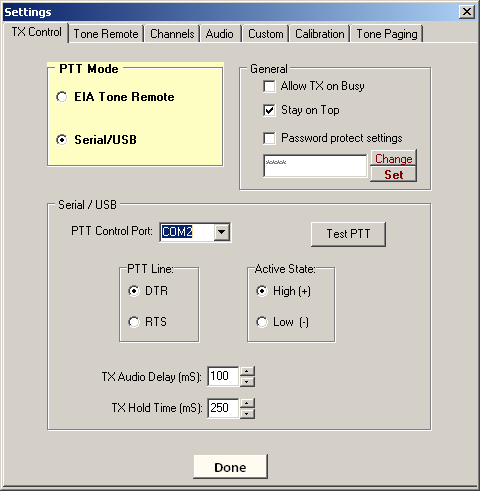
PTT Mode
1. The first step is to select Tone or Serial control (PTT Mode).
2. For Serial mode, use the settings on the lower portion of this tab (Tone remote settings are found on the next tab below).
Serial/USB
3. If a USB adaptor is used, it must be installed before attempting to configure DISPATCHER. COM port numbers may be found in Windows Device Manager.
4. Select the PTT Control Port. Numbers 1 - 64 are supported. If the port is in use or not available, an error message will appear. Once a valid port has been selected, it will be held open by DISPATCHER and will not be available for use by other programs.
5. Now choose PTT control line (pin) and active state. NOTE: Voltage will be +/- 12V on an RS-232 port or 5V on a USB adaptor. On a DB-9 connector, DTR is pin 4, RTS is pin 7, and ground is on pin 5.
6. Set TX Audio Delay - this is the time between PTT activation and beginning of audio signals (does not apply to voice, only tone signals). For most applications, this setting is usually not critical.
7. TX Hold Time - Keeps the transmitter keyed for the selected time period after tone signals have ended. Not required for most applications.
8. Finally, test your settings with the "Test PTT" button. If everything is set up and wired correctly, this button will momentarily key the transmitter while pressed.
1. Allow TX on Busy - Determines whether operator will be allowed to transmit when a channel is busy.
2. Stay on Top - When checked, the main screen will stay on top of all other open windows.
3. Password protect settings - It is recommeded to set a password after technician has completed setup and testing. If password is lost, contact ComTekk Tech Support.
4. Click "Change" then type in new password. Click "Set" to save password.
3. Tone Remote Settings
These adjustments are provided for customization and convenience, allowing for the most precise signal emulation. Under normal circumstances, you should not need to change these settings.
Be aware that when sharing a control line with another tone console, channel changes by another dispatch position will not be registered i.e., if dispatcher 'A' changes the channel (frequency), dispatcher 'B' will not see an indication the channel was changed.
NOTE: Tone Remote control may not function properly in Windows Vista.
Recommended Equipment:
- Transmission Impairment (TIMS) Test Set, such as the Ameritec AM44
- Oscilloscope
- Shielded cables with appropriate connectors/adaptors
Connect computer sound device output to 600-ohm line or circuit to be tested and to scope or TIMS.
*WARNING* Do Not connect sound device directly to a POTS line or other circuit which could have voltage present. This could damage the computer as it does not provide any protection against high voltage or transient surges. Please Contact Us if you need a line interface adaptor.
Adjustment Procedures:
NOTE: These settings should only be altered by a qualified radio service technician.
1. Open the Settings window (Tools->Settings or Ctrl-S). In the Settings window, click on the Tone Remote tab.
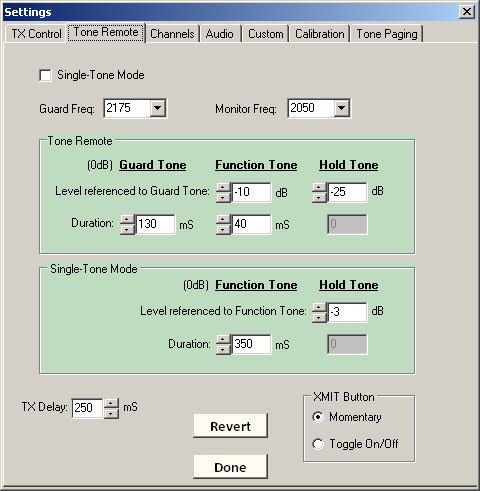
2. Select the desired Guard and Monitor tone frequencies. Select Single Tone Mode if desired. Note that if Single-Tone Mode is selected, only those fields below will be accessible, and vice-versa for Dual-Tone Mode.
3. To set Hold Tone level, click the PTT button to begin transmitting. Note the signal level on test equipment. Adjust the Windows Volume and Mixer controls as needed to achieve desired signal output**.
Using the up/down buttons for each field, adjust dBm level as required for single or dual-tone mode in the Settings screen. NOTE: To see the change, you must stop transmission, then start again. To restore the original stored values, click the Revert button; To save the new values, click OK.
4. Guard Tone and Function Tone adjustments - set tone levels if needed (EIA standard settings are used by default, and normally should not require adjustment).
5. Adjust dual or single-tone durations, then adjust levels if needed (EIA standard settings are used by default, and normally should not require adjustment).
6. The "TX Delay" time determines how long DISPATCHER will delay before transmitting secondary signals, such as tone-burst or alert tones. At a minimum, this setting should typically be slightly longer than the total of the Guard Tone Duration plus Function Tone Duration. About the only exception to this rule would be when transmitting over a dedicated link to control a remote base station.
7. XMIT Button - Select Momentary (default) to stop transmitting when button is released, or Toggle for click-on, click-off control.
**To set output level, use the TX/Master Volume control on the Audio settings tab. This will control the maximum output of the sound device. dB level settings are relative to the TX/Master Volume setting.
Note: All settings are saved in the INI file upon exiting the program.
4. Tone Channel Settings
1. Open the Settings window (Tools->Settings or Ctrl-S) and click on the Channels tab. NOTE: In Serial/USB mode, these settings have no effect, other than to se the Channel Name.
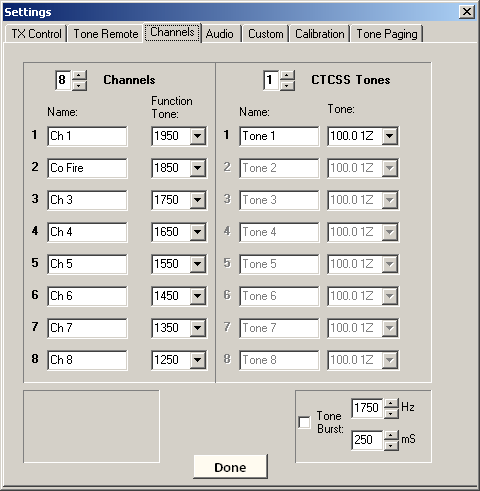
2. First, select the desired number of channels (1-8), and the number of CTCSS tones (0-8). Note the corresponding number of channel settings fields below will be enabled, with the rest "grayed-out."
3. Now type in the display name for each channel (left-hand column) as you want it to appear on the console. Select the corresponding function tone frequency from the drop-down box to the right of the names.
4. Repeat this procedure for the CTCSS Tone (repeater access) channels in the right-hand column, selecting the desired tone frequency for each.
5. If a tone-burst signal is required for repeater access, click the "Tone Burst:" checkbox to enable. Then select the desired frequency and duration using the up/down buttons. It may be necessary to adjust the TX Delay time in the Tone Remote settings window.
Note: All settings are saved upon exiting the program.
5. Audio Setup
ComTekk Mixer:
If the Mixer is not visible, click the Mixer toolbar button, or select the "View" menu, then click "Mixer." There will be a check-mark next to the menu item showing whether it is visible.
First, select the "TX Audio Device", "MIC Audio Device" and "RX Audio Device." Generally, the TX and MIC devices should be on the same sound card. RX Audio may be fed into a different sound card if installed. All tones will be sent to the TX Audio Device. RX busy and RX muting utilize the selected RX Audio Device.
NOTE: In Windows Vista, individual input/output jacks may be selected. On all earlier versions of Windows, only the sound card may be selected. By default, the system's DEFAULT sound device is selected for all three.
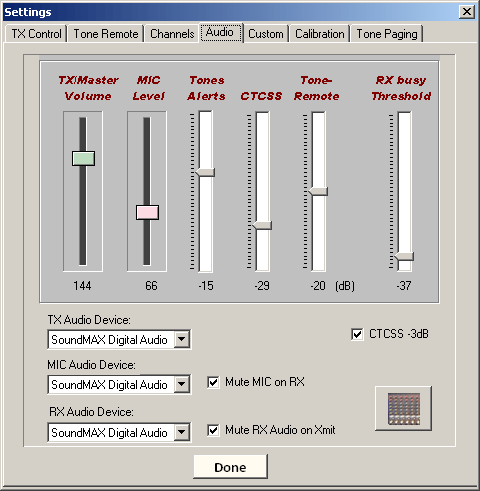
TX/Master Volume controls the TX Audio Device output. All other levels, except MIC are relative to this setting. It is recommended the Windows taskbar volume icon be disabled to prevent operators from altering this setting. This setting is found in the Windows Sounds Control Panel.
Use the sliders to adjust the relative output level for each corresponding generator or encoder.
The control labeled "Tones Alerts" controls the level of Paging tones, Alert tones and Tone Burst, if used.
Audio Control Settings
Use the "CTCSS -3dB" checkbox to cut the PL-tone generator output in half, thus making adjustment much easier at low levels.
The "Tone-Remote" slider sets the relative level of the tone-remote signal generator during transmit and when function keys are activated, such as "Monitor" or changing a channel.
"RX Busy Threshold" sets the input level required to activate the receive "RX" indicator on the main console screen. It does NOT affect the actual volume of the input, which is set using the Windows Volume Control below. NOTE: for RX Indicator to function, you must select the appropriate sound card input "RX Audio Device."
The "Mute Mic on RX" checkbox, when checked, causes the microphone input to be muted while console is in receive mode. If PTT "Transmit" is activated, the mic will be opened to allow voice audio to pass over the line to the transmitter.
"Mute RX Audio on TX" when checked, will mute the corresponding RX Audio Device to prevent possible feedback or echo from the receiver while transmitting.
![]() If needed, the Windows Audio/Mixer control panel may be accessed with this button. This is helpful for viewing your system's available audio devices.
If needed, the Windows Audio/Mixer control panel may be accessed with this button. This is helpful for viewing your system's available audio devices.
6. Tone Paging
ComTekk DISPATCHER has a flexible paging encoder, compatible with virtually any 1-tone, 2-tone (1+1) or 3-tone format.
NOTE: Duo-tone formats such as QuickCall-I, DTMF and SELCAL are not currently supported.
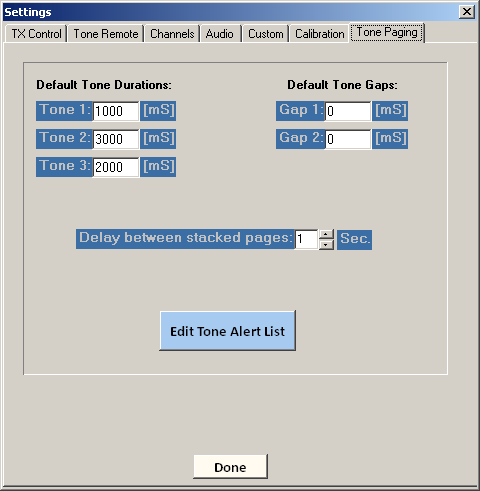
Default Tone Durations and Gaps - This determines the default tone lengths and gap between tones. The most common format in use in the US today is 2-tone (1+1), 1sec. + 3sec, no gap. This happens to be the default setting. For 3-tone formats, set Tone 3 duration and Gap 2. [1,000 mS = 1.0 second]
Delay between stacked pages - Determines time delay between repeated or stacked tone sets when paging out 2 or more stations at a time.
To set up or modify paging memories, click "Edit Tone Alert List."
The number of available memories is dependent on the license purchased. In the trial version, only 2 are available. 25 or more memories may be entered on licensed copies.
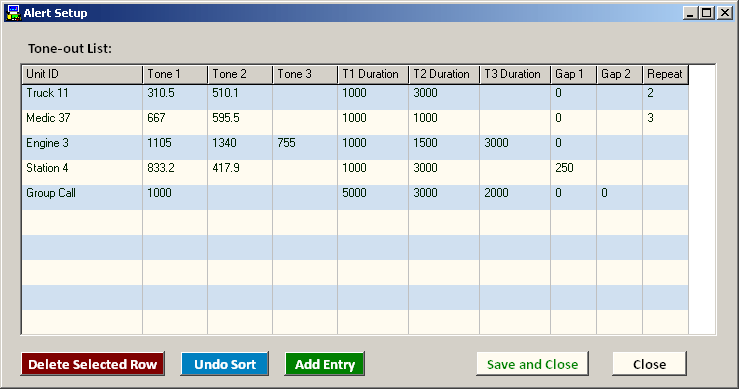
Fields:
Unit ID - This is the unit or station name that will appear in the drop-down list on the operator's screen.
Tones, Durations, Gaps - When adding an entry, these fields will be populated with the default settings defined in the previous section, but may be changed at will to accommodate multiple formats. Any blanks will be assumed to be zero values.
Repeat - determines how many times a single selected page will repeat. Does not apply when stacking 2 or more Units.
Editing:
To edit an entry, simply double-click anywhere within that row. The Edit Window will appear:
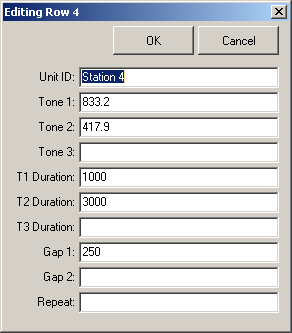
Click "OK" or press Enter when finished.
Buttons:
Delete Selected Row - Deletes the highlighted row. Be careful though, there is no "undo" for this function. If you make a mistake you can close without saving, exit the program, then restart DISPATCHER to restore the saved list.
To sort all entries, click on the column name. For example, click "Unit ID" to sort by unit name. Click again to reverse sort order.
Undo Sort - restores original sort order. Will not work after saving.
Add Entry - Adds a new entry at the next available empty row.
Save and Close - Saves the current alert list.
Close - Exits the alert list screen without saving. You can save at any time by returning to this screen while the program is running.
7. Sound Card Calibration
Computer sound cards vary greatly in quality and design. They have their own time-base which controls the A/D and D/A sampling rate, which in turn directly affects the frequency. The calibration routine allows for compensation for time base error, thus allowing accurate frequency synthesis.
Recommended Equipment:
- Calibrated Frequency Counter with resolution to 1Hz
- Shielded cable with appropriate connectors
CALIBRATION INSTRUCTIONS:
1. Connect output of sound card to a calibrated frequency counter.
2. From ComTekk, open the Settings window, using the toolbar or or select Settings from the File menu. Click START. Using the Mixer panel and Windows volume control (Press Ctrl+V or on the Tools menu, select WinVolume), adjust output as needed to get a steady reading on counter, typically at least 1Vp-p. Set counter to read down to 1Hz.
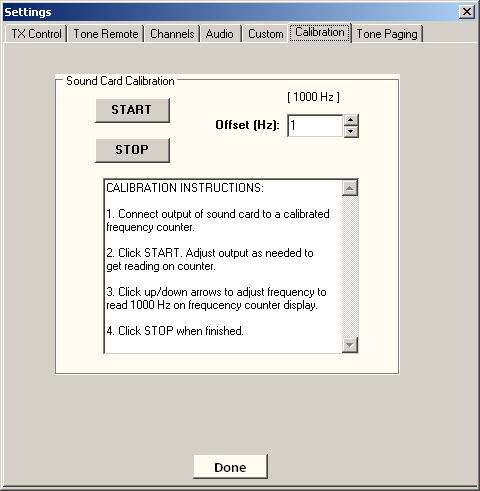
3. Click up/down arrows to adjust frequency to read 1000 Hz on frequency counter display. Adjustment range is limited to +/- 100Hz. If this is not adequate, the sound card in use is likely not reliable and a different computer should be used.
4. Click STOP when finished. The difference if any has been saved and will be used to adjust all the signal generators within ComTekk.
Note: All settings are saved upon exiting the program.
8. Custom Settings
1. Open the Settings window (Tools->Settings or Ctrl-S), then click on the Custom tab.
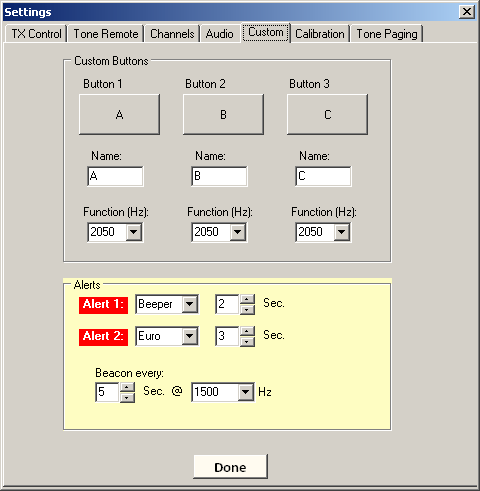
2. The three user-programmable function keys may be set here. Enter the the button label in the "Name" box below each button. A preview of the button can be seen above. Then select the desired function tone frequency in the drop-down box below each button.
3. The two Alert console keys are also set in this screen. Select the alert type using the drop-down boxes and the duration in seconds for each alert button.
4. Finally, the beacon (marker tone) delay and attention-signal frequency are selected at the bottom of the page. Click "Done" when finished.
Note: All settings are saved upon exiting the program.